PlantCFG: Database of Candidate Flowering Genes in Plants
——A comprehensive database with web tools for analyzing candidate flowering genes in multiple plants
Welcome To PlantCFG
A comprehensive database with web tools for analyzing candidate flowering genes in multiple plants.
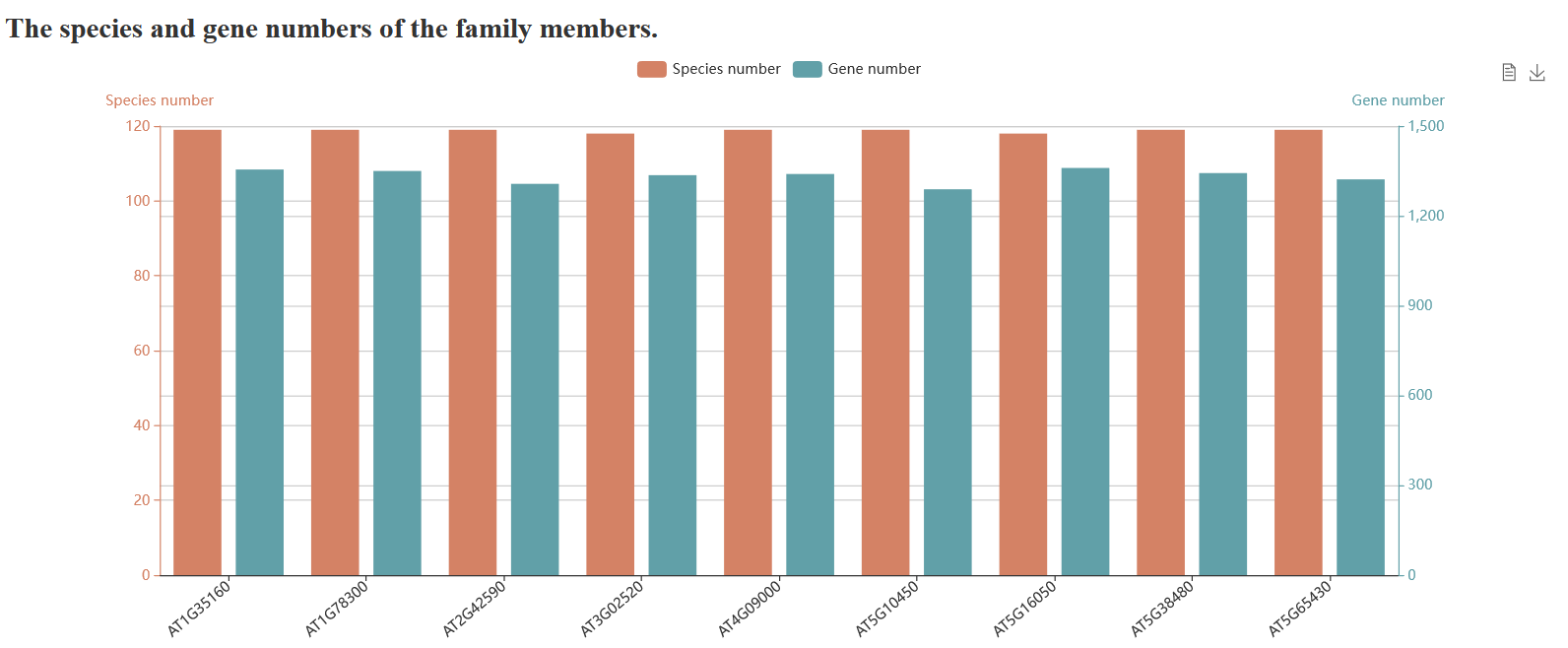
PlantCFG, a multi-species plant candidate flowering gene database, contains 112 species from 10 plant families. We performed
a careful literature survey and 459, 71, and 112 reported flowering genes were curated in Arabidopsis
thaliana, Glycine max, and Oryza sativa, respectively. The candidate flowering genes in
other species were identified by using a combination of sequence similarity and conserved domain based
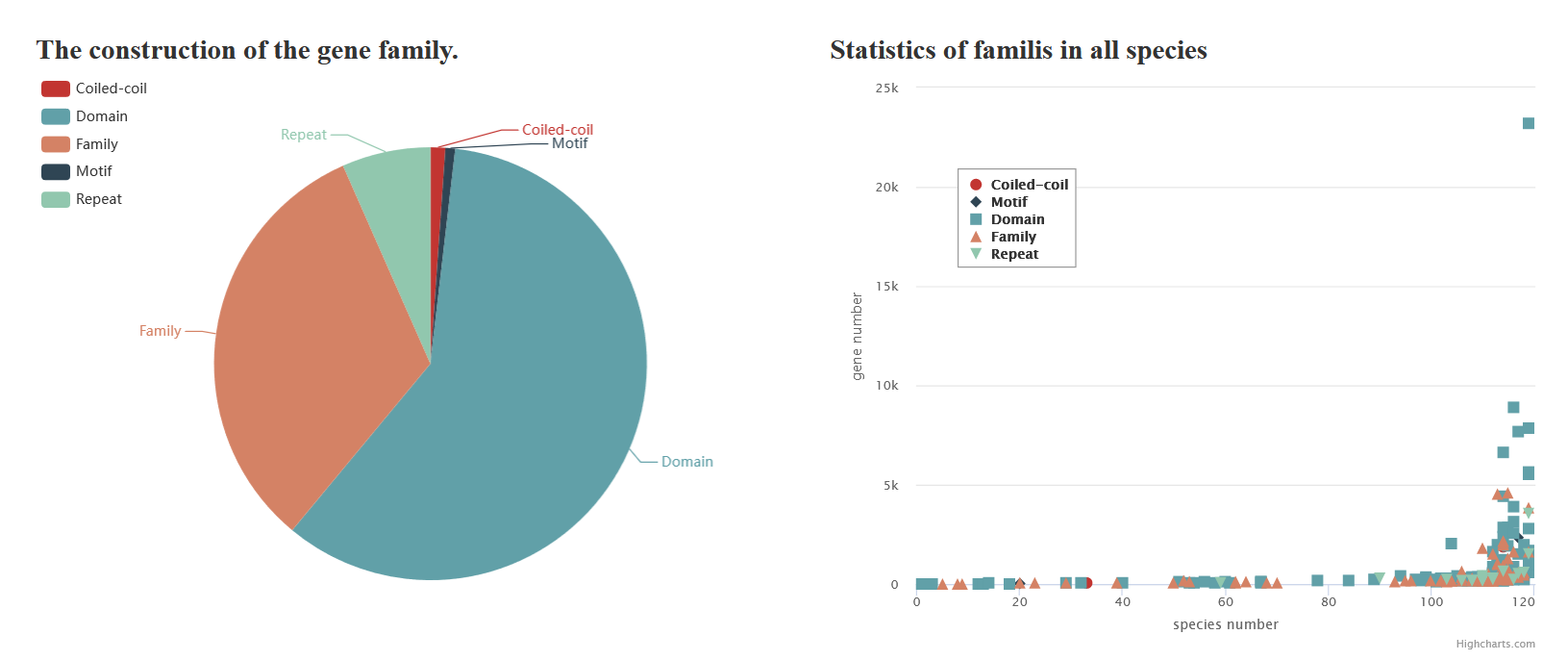
approaches. It contains 82,104 candidate flowering genes, which were classified into 372 protein classes and 62 gene families. PlantCFG aims to
collect,
organize, display and compare flowering genes in multiple plants, including the following: (i) query the basic
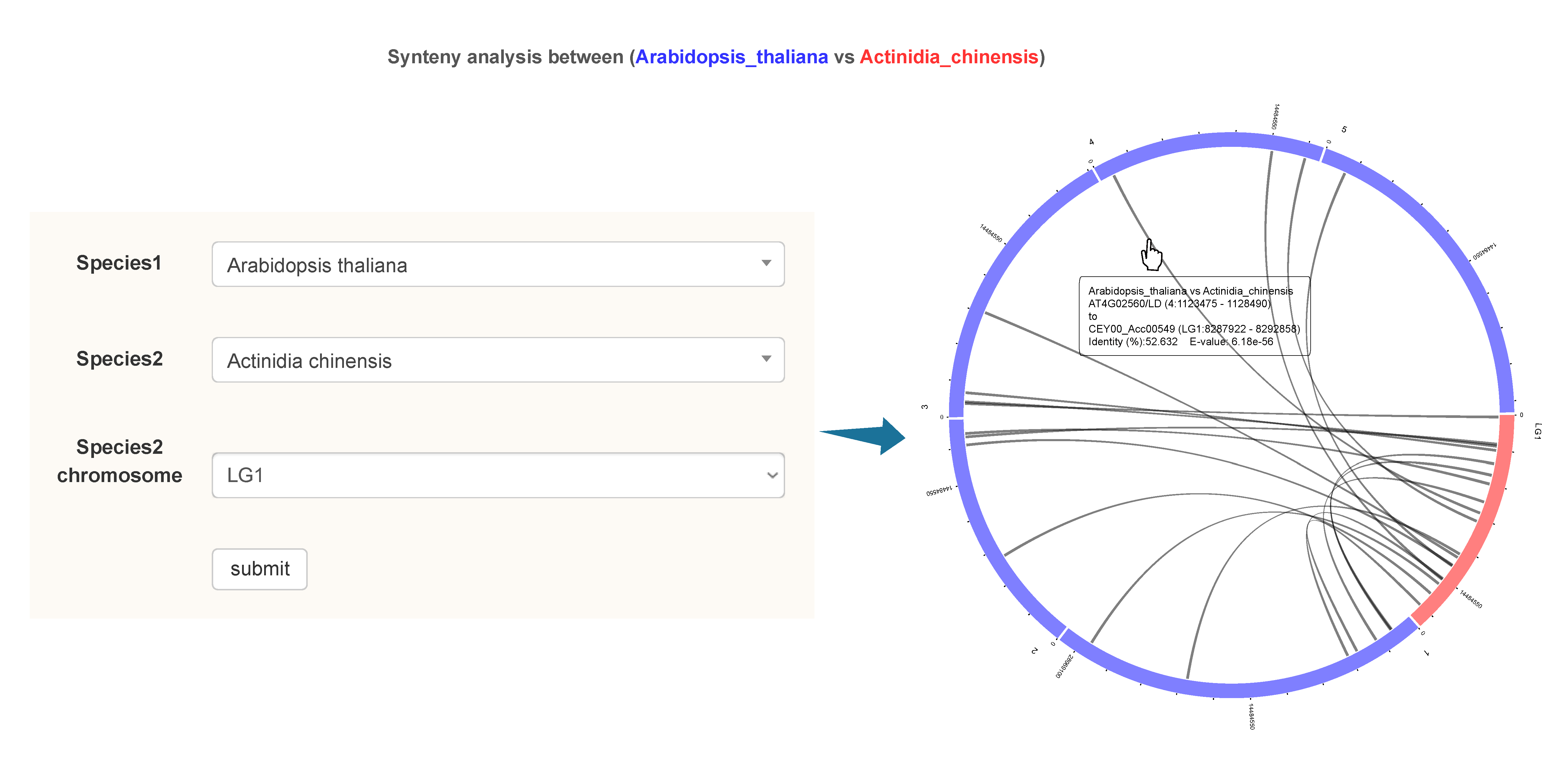
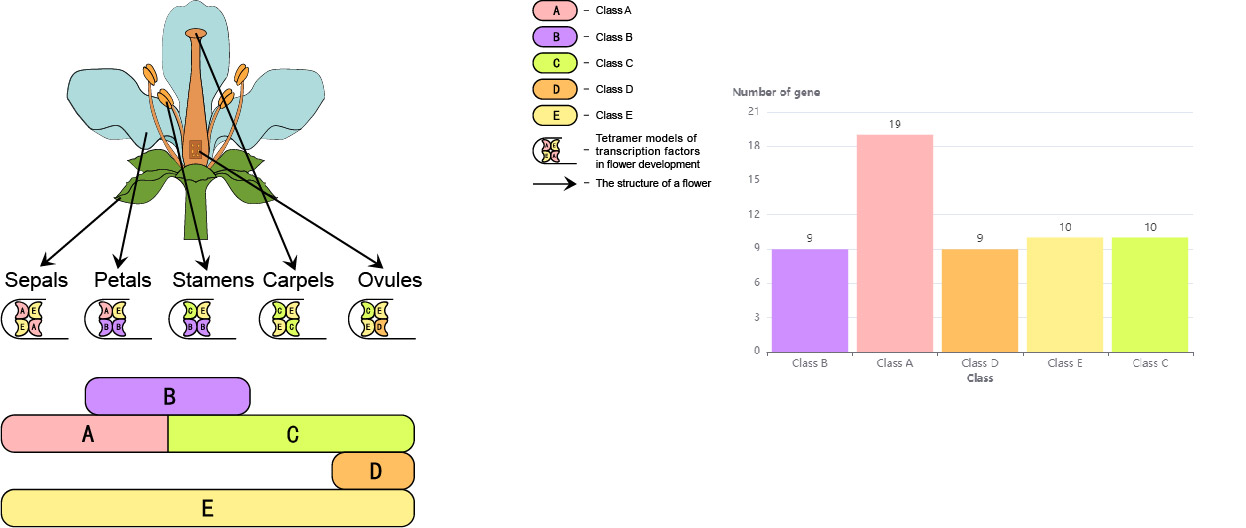
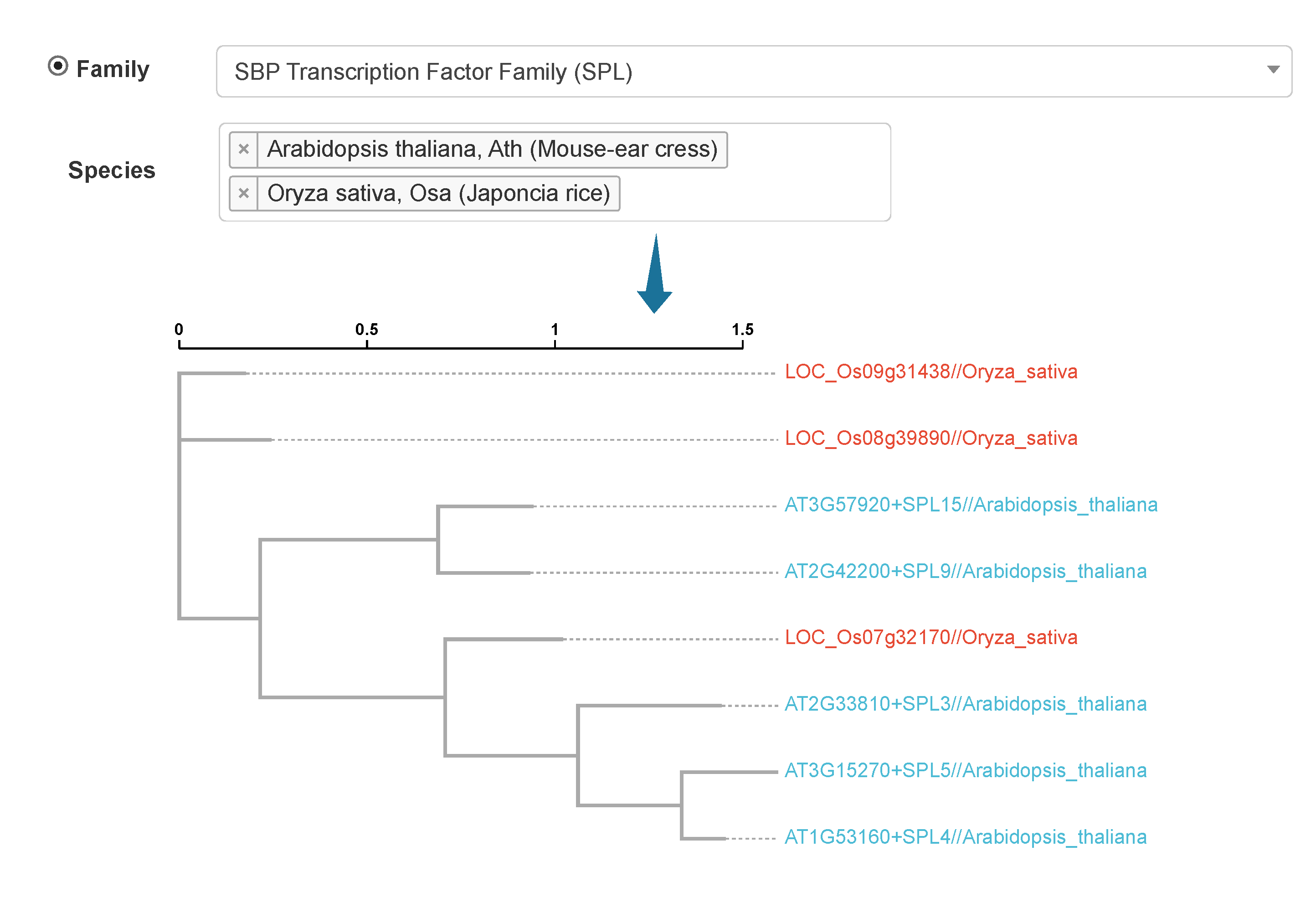
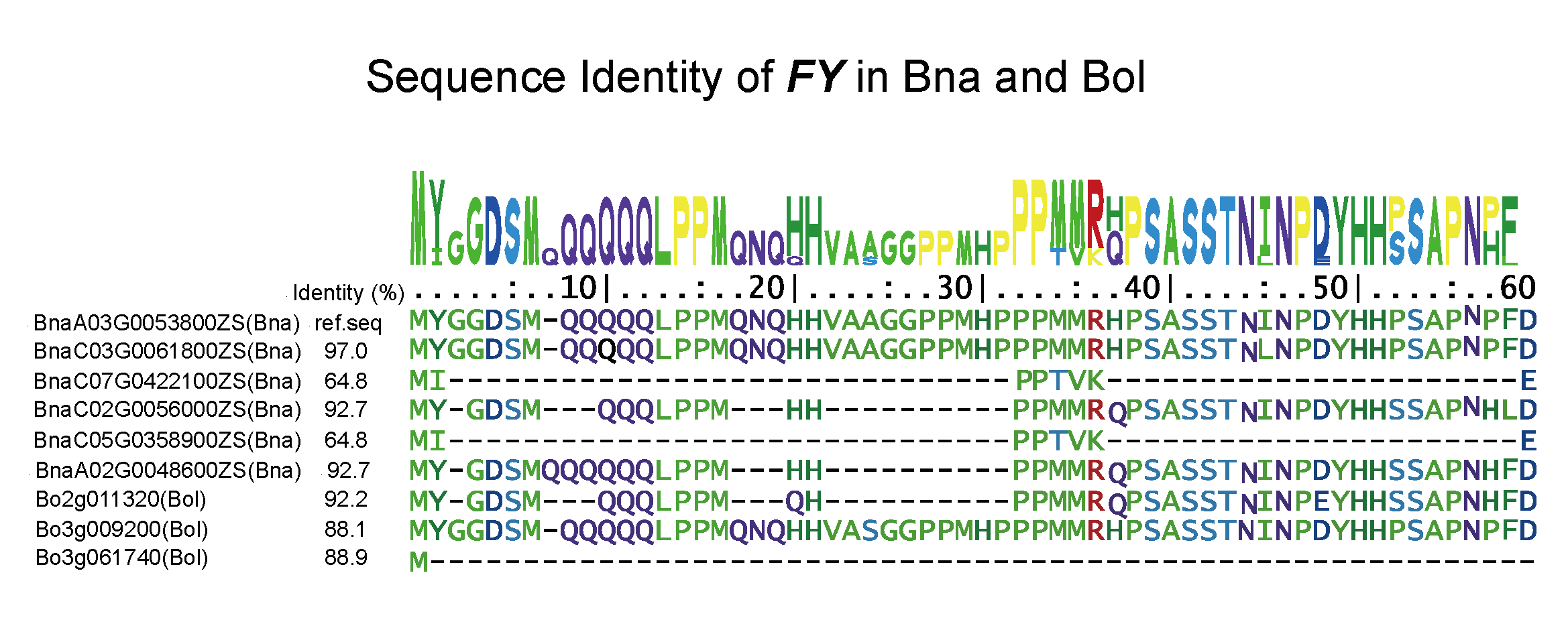
information of candidate flowering genes in 112 plants; (ii) explore the functions of genes involved in the ‘ABCDE’ model; (iii) carry out collinearity relationship, phylogenetic, sequence identity, and Ka/Ks analyses of candidate
flowering genes in different species; and (iv) browse, search and batch download flowering gene lists and
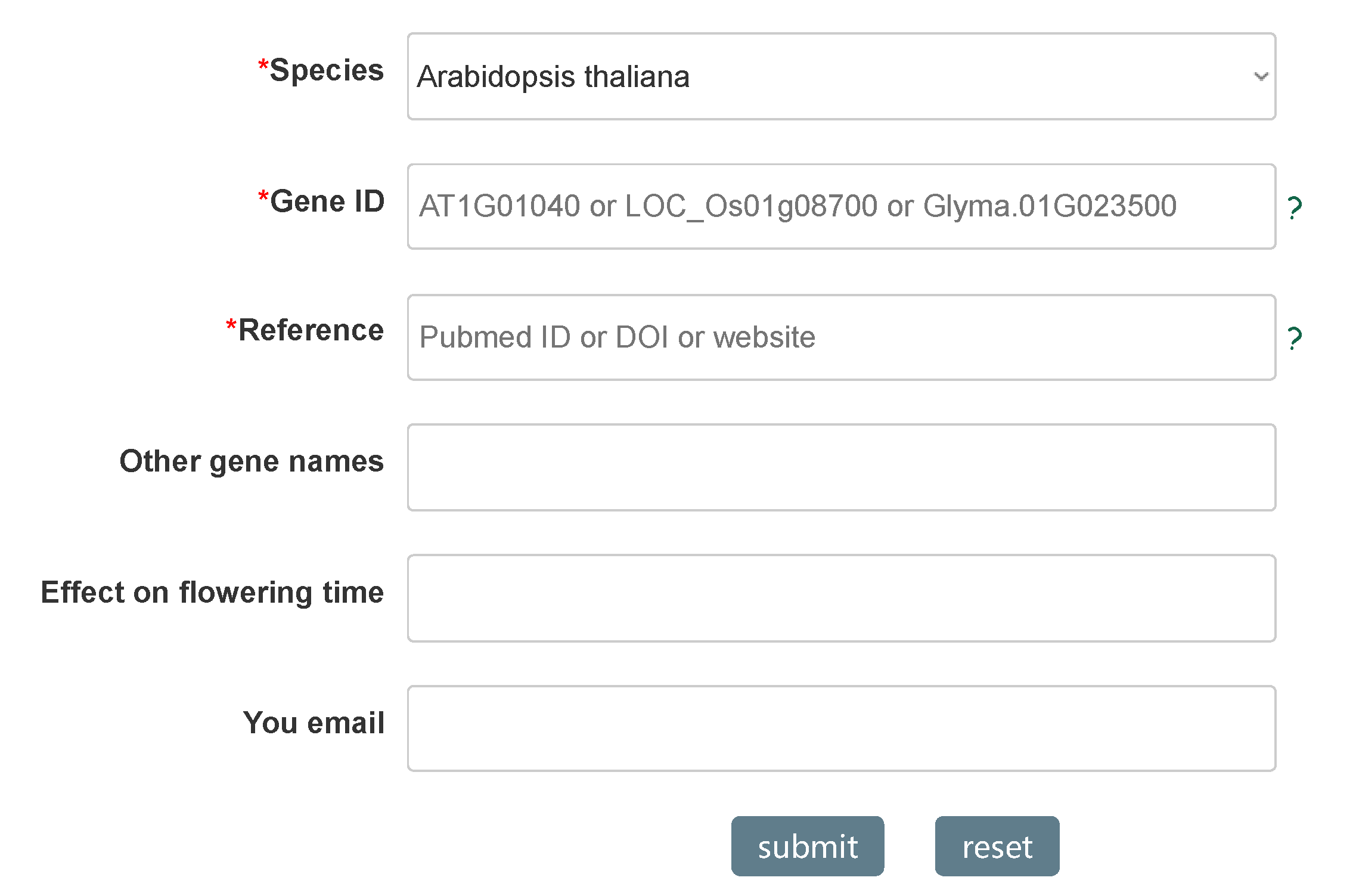
sequences. Furthermore, we provide a Submit module, where users can submit flowering gene, which will
be reviewed and periodically updated to the database.
(ii) That most flowering time regulatory pathways in distant groups are likely to involve different genes, and that positive flowering time regulators in some species could have an opposite function in others.
Notice
(i) The lists provided here are candidate flowering genes inferred from orthologous groups which DO NOT represent flowering genes from experimental work (in most species);(ii) That most flowering time regulatory pathways in distant groups are likely to involve different genes, and that positive flowering time regulators in some species could have an opposite function in others.
How to cite us
Dongxu Liu, Jiawei Li, Shengbo Wang, Tingting Huang, Fangting Tao, Yuchen Lin, Wei Lin, Xinle Zhao, Yiming Huang, Yupeng Jia, Zhiquan Yang, Chengfang Luo, Qiang Zhu, Wing-Kin Sung, Jian Wu, Qing-Yong Yang PlantCFG: A comprehensive database with web tools for analyzing candidate flowering genes in multiple plants. PLANT COMMUNICATIONS (2023),doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xplc.2023.100733Search the candidate flowering genes
e.g. AtFLC or OsHd3a or GmFT2a or BnaA10G0244800ZS or Actinidia chinensis or Class A
or
PF00249 or C2H2 Transcription Factor Family
Species summary